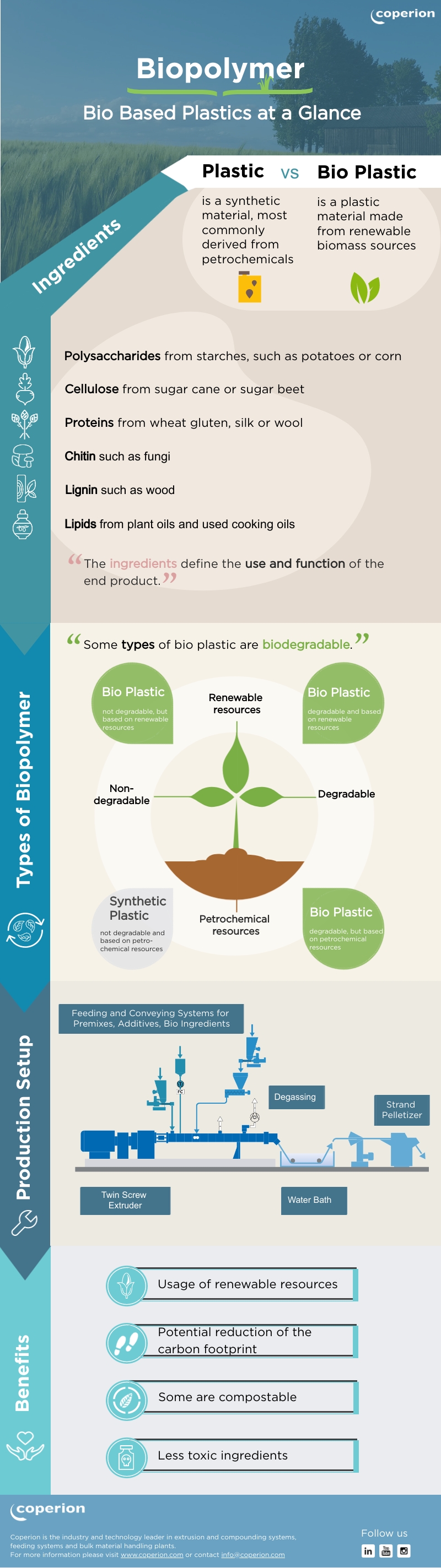
Generally, there are many natural resources that can be used for the production of biopolymer products. The most common ones are polysaccharides and cellulose which are derived from starches as well as sugar canes. But also proteins, chitin, lignin and lipids are used for the processing of bio based plastic.
Nonetheless, it is important to understand that not all ingredients are equally suitable for a specific application. The ingredient basically defines the use as well as the function of the end product and whether or not it can be composted. While single-use packaging can often be composted at home, at least in theory, other compositions of ingredients may require industrial composting or are not compostable at all. In this connection, polymers can be categorized in different types depending on the resources being used and whether or not they are degradable. Based on this classification there are three sorts of bio plastic:
- Bio plastic that is derived from renewable resources, but which is not degradable
- Bio plastic that is derived from renewable resources and that is indeed degradable
- Bio plastic that is in fact biodegradable but based on petrochemical resources (e.g. polybutyrate)
The production setup of bio plastic usually consists of feeding and conveying systems, a twin screw extrusion system, a degassing system, as well as a strand pelletizer. Thanks to the modular design of the process section and its excellent homogenization, the ZSK twin screw extruders from Coperion are suitable for a wide range of bio plastic applications. Along with the extensive feeder portfolio from Coperion K-Tron and our in-depth process know-how, manufacturers of bio plastics can expect a fully integrated high-performance system when working with Coperion.
Biopolymer has various benefits in comparison to conventional plastic materials. First and foremost, it is based on renewable biomass and not dependent on limited fossil resources. At the same time bio plastics actively contribute to the reduction of CO2 emissions. Furthermore, some types of biopolymer are also compostable and degrade in a specific period of time and under certain conditions. Thanks to its natural properties, bio plastic contains less toxic materials than synthetic polymer.
Even with all these advantages, it is important to keep in mind that also bio plastic requires a lot of energy in the production process. In addition, most bio based plastic products require industrial composting in order to fully degrade. Since consumers normally cannot differentiate between bio plastic and conventional plastic, both types usually end up in the same bin – as a result, bio plastic waste never reaches a composting plant in many cases. Therefore, biopolymers are not always a more sustainable alternative to conventional plastic materials.
 Coperion
Open navigation
Coperion
Open navigation